Report
Results ready 4-6 hours (after completion of the test).
Extra
SCAN TIME: maximum of 30 minutes in the machine.
Setup
All working days
Test in Brief
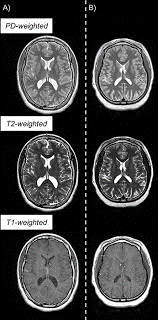
An imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radiowaves to produce images. Unlike X-rays and CT scan, it does NOT use ionizing radiation. The patient lies on a motorized table which will move the patient into the scanner which resembles a giant doughnut (like a tunnel that is open at both ends).
Exam Requirements
Remove all metal objects (e.g. watches, jewellery); patient should complete the safety questionnaire that is provided prior to the procedure; the scanner is a tunnel that is open at both ends; headphones or earphones will be used to muffle the sounds produced by the scanner. Occasionally, a special dye (contrast media) is administered through the vein. Patient should lie still till the end of procedure/exam to avoid getting blurry images.
Instructions For Referring Doctor Or Institution
Please state clinical indication for the test on the request form; for NHIF & other insurance clients, provide the necessary documentation in full inclusive of stamps and referrer’s name/ signature/ board registration details where required. In case of NHIF queries/ clarifications, call 0785 033335 (Nakuru).
Instructions For Radiographer
Guide the patient when filling the safety questionnaire to identify any contra-indications before the procedure/exam.
Method
Patient is placed in the MRI magnetic bore; radiofrequency is sent in depending on the sequence/ time; radiofrequecy is turned off; images are reconstructed on the MRI Console & assessed for good radiographic quality. Images are then reviewed by the radiologist. A comprehensive report detailing the patient name, gender, age, procedure date, procedure name and findings is provided.
Usefulness /Advantages
A brain MRI can help diagnose conditions such as bleeding, swelling, problems with the way the brain developed, tumors, infections, inflammation, damage from an injury or a stroke, or problems with the blood vessels , Headaches or seizures.