CT Scan
CT scan is a diagnostic procedure that uses ionizing radiation to acquire cross sectional images of the body parts in slices. This includes:
- head
- Neck
- Lungs
- CT Angiography
- Cardiac
- Abdomen
- Pelvis
- The skeleton and extremities.
Cardiac CT scan is performed to gain knowledge about the anatomy and the functional parts of the heart whereas CT angiography is used to visualize the arteries and veins—throughout the human body. Contrast is used as a dye in this case. This helps to rule out blockages, aneurysms (dilations of walls), dissections (tearing of walls), and stenosis (narrowing of vessel).
Depending on the body parts scanned, various prior preparations are done. The doctor may request a contrasted exam as well.
CT scan is also useful during CT guided biopsies where the doctor cannot feel the lump or mass as well as monitor the effectiveness of certain treatments and the general prognosis.
Typically a CT scan appointment takes short time. For a CT scan with oral contrast, it could take up to 1 hour and 30 minutes. If you are receiving CT scan IV contrasts, for abdominal CT scan, do not eat or drink 6 to 12 hours prior your exam. You may continue to drink water if you prefer.
CONTRAST
Doctors may request for a contrasted or non-contrasted CT scan. Most contrasts used are iodine-based.
Using contrast material can also help to obtain functional information about tissues as well as differentiating it with the surrounding structures. One may be requested to do renal function tests prior to the examination to assess suitability for contrast administration.
AFTER THE PROCEDURE
After the exam you can return to your normal routine. If you were given contrast material, you may receive special instructions. After the scan, you are advice to drink lots of fluids to help your kidneys remove the contrast material from your body.
Always remember to inform the technician of any allergies, if you have any medical conditions or recent illnesses this is in case your doctor requested for a contrasted CT scan as well as preparation for any possible outcome. Patients can take their prescribed medication as usual; you may be required to bring a list of your medications to your appointment that includes the name of the medication and the dose.
PRECAUTION.
Any female of child bearing age must inform the doctor if they are expectant or are currently lactating.
Benefits of a CT Scan
- CT scanning is painless, noninvasive, and accurate.
- A major advantage of CT is its ability to image bone, soft tissue, and blood vessels all at the same time.
- Unlike conventional x-rays, CT scanning provides very detailed images of many types of tissue as well as the lungs, bones, and blood vessels.
- CT exams are fast and simple. In emergency cases, they can reveal internal injuries and bleeding quickly enough to help save lives.
- CT has been shown to be a cost-effective imaging tool for a wide range of clinical problems.
- CT is less sensitive to patient movement.
- Unlike MRI, an implanted medical device of any kind will not prevent you from having a CT scan.
- A diagnosis determined by CT scanning may eliminate the need for exploratory surgery and surgical biopsy.
- No radiation remains in a patient’s body after a CT exam.
- The x-rays used for CT scanning should have no immediate side effects.
Patient preparation
- Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing to your exam. You may need to change into a gown for the procedure.
- Metal objects, including jewelry, eyeglasses, dentures, and hairpins, should be removed prior to your exam.
- CT exams will require you to remove hearing aids and removable dental work. Women will need to remove bras containing metal underwire.
- Your doctor may instruct you to not eat or drink anything for a few hours before your exam if it will use contrast material.
- Tell your doctor about all medications you are taking and if you have any allergies and any other underlying medical condition.
- Women should always inform their physician and the CT technologist if there is any possibility that they may be pregnant.
- You’ll be required to fill a CT questionnaire prior to the exam as well as a consent form in case the doctor suggest the used of contrast(dye).
- Exams with IV contrast (dye) require renal panel (blood test) results
Test procedure and duration
- It is always necessary to consult a doctor before a CT scan, because due to the radiation exposure, the CT scan can only be performed on the basis of a medical recommendation.
- CT scanners can obtain multiple and thinner slices in less time. This results in more detail.
- Modern CT scanners can image large sections of the body in just a few seconds, and even faster in small children.
- Speed is especially beneficial for children, the elderly, and critically ill – anyone who finds it difficult to stay still, even for the brief time necessary to obtain images.
- During the scan, the radiology technician will talk to the person via a speaker to let them know them when the scan is starting.
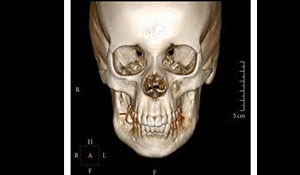
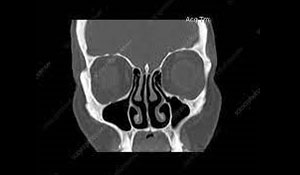
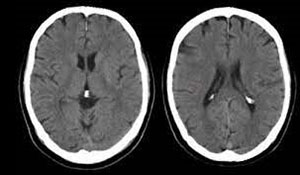
CT HEAD
- The average CT scan of the head takes no more than 10 minutes.
- A CT scan of the head is useful for helping a doctor assess damage after an accident or head trauma.
- It also allows them to look for brain abnormalities, such as tumors and skull defects.
- Doctors consider CT scans to be relatively safe and noninvasive procedures, even though they involve exposure to radiation
Results
- A medical specialist called a radiologist will examine the imaging scans, looking for any abnormalities in the brain and surrounding tissues. They will write a report of their findings and send it to the doctor who ordered the scan.
- If a person is in the hospital and undergoing the scan as an emergency, the radiologist will report any immediately concerning results as quickly as possible.
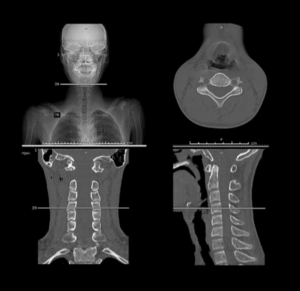
CT NECK
A CT scan of the neck can give your doctor information about your neck, throat and tonsils, infection or tumors and other structures in the neck area.
What happens during the test?
- You will lie on a table that is attached to the CT scanner.
- The table will slide into the round opening of the scanner.
- The table will move during the scan. The scanner moves inside the doughnut-shaped casing around your body.
- You may be alone in the scanning room, but a technologist will be watching you through a window and talking with you during the test.
How long does the test take?
The actual test only takes about 10 minutes.
What happens after the test?
- You will probably be able to go home right away.
- You can go back to your usual activities right away.
- Drink plenty of fluids for 24 hours after the test if dye was used, unless your doctor tells you not to.
- A medical specialist called a radiologist will examine the imaging scans, looking for any abnormalities in the brain and surrounding tissues. They will write a report of their findings and send it to the doctor who ordered the scan.
CT CHEST
A CT scan of the chest can give your doctor information about your lungs, your heart, and other structures in your chest.

What happens during the test?
- You will lie on a table that is attached to the CT scanner.
- The table will slide into the round opening of the scanner.
- The table will move during the scan. The scanner moves inside the doughnut-shaped casing around your body.
- You may be asked to hold your breath for short periods.
- You may be alone in the scanning room, but a technologist will be watching you through a window and talking with you during the test.
What happens after the test?
- You will probably be able to go home right away.
- You can go back to your usual activities right away.
- Drink plenty of fluids for 24 hours after the test if dye was used, unless your doctor tells you not to.
- A medical specialist called a radiologist will examine the imaging scans, looking for any abnormalities in the brain and surrounding tissues. They will write a report of their findings and send it to the doctor who ordered the scan.
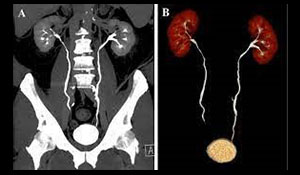
CT ABDOMEN
A CT scan of the belly can help find problems such as kidney stones, infected pouches in the colon (diverticulitis), and appendicitis. It also helps find tumors and abscesses.
Inform your doctor if;
- You are or might be pregnant.
- You are allergic to any medicines.
- You have diabetes.
- You take metformin.
- You are breastfeeding.
- You get nervous in confined spaces.
- You may need medicine to help you relax.
- You have had an X-ray test using barium contrast material in the past 4 days.
NB:
- You may be asked to not eat any solid foods starting the night before your scan. (6 to 8 hours fasting).
- If dye is used, you may feel a quick sting or pinch when the IV is started. The dye may make you feel warm and flushed and give you a metallic taste in your mouth.
- The test will take about 60 minutes of taking oral contrast. Most of this time is spent getting ready for the scan.
- The actual test takes a few minutes.

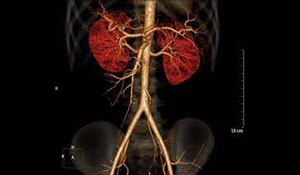
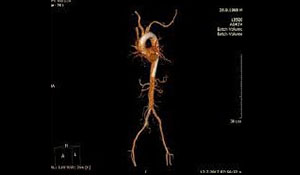
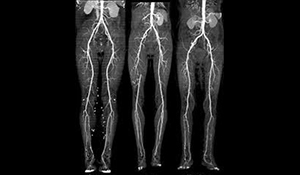
CT ANGIOGRAM
A computed tomography angiogram (CT angiogram) is a test that uses X-rays to provide detailed pictures of the heart and the blood vessels that go to the heart, lung, brain, kidneys, head, neck, legs, and arms.
This test can show narrowed or blocked areas of a blood vessel. It can also show whether there is a bulge (aneurysm) or a buildup of fatty material called plaque in a blood vessel.
During a CT angiogram, you lie on a table that passes through a doughnut-shaped opening in the scanner. A special dye (contrast material) is put in a vein (IV) in your arm or hand to make the blood vessels easier to see on the scan.

CARDIAC CT
What is it?
A CT of the heart looks at the structures and blood vessels of the heart.
During the test, you lie on a table that passes through a doughnut-shaped opening in the scanner. A special dye (contrast material) may be put in a vein (IV) in your arm or hand to make the blood vessels easier to see on the scan.
Why is this test done?
A CT of the heart is done to look at the structures and blood vessels of the heart. These may include:
- The heart muscle and the sac around the heart (pericardium).
- The heart valves.
- The coronary arteries. These are the blood vessels that bring blood to your heart muscle.
- The blood vessels that carry blood from the lungs to the heart.
- The aorta. It’s the large blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
How do you prepare for the test?
In general, there’s nothing you have to do before this test, unless your doctor tells you to.
You may be asked not to eat or drink anything for several hours before the test. Your doctor will let you know if there are certain foods or liquids you should avoid.
How is the test done?
Before the test
- You may have to take off jewelry.
- You may need to take off some of your clothes. You will be given a gown to wear during the test. If you do leave some clothes on, make sure you take everything out of your pockets.
- You may have contrast material (dye) put into your arm or hand through a tube called an IV.
During the test
- You will lie on a table that is attached to the CT scanner.
- Small pads or patches (electrodes) will be placed on your skin on each arm and leg and on your chest. The electrodes are hooked to a machine that traces your heart activity onto a paper.
- The table will slide into the round opening of the scanner and move slightly while the scanner takes pictures. You may hear a click or buzz as the table and scanner move.
- You will be asked to hold still during the scan. You may be asked to hold your breath for short periods.
- You may be alone in the scanning room. But a technologist will watch you through a window and talk with you during the test.
How does the test feel?
The test will not cause pain, but some people feel nervous inside the CT scanner.
If a medicine to help you relax (sedative) or dye is used, you may feel a quick sting or pinch when the IV is started. The dye may make you feel warm and flushed and give you a metallic taste in your mouth. Some people feel sick to their stomach or get a headache. Tell the technologist or your doctor how you are feeling.
How long does the test take?
The test will take about 30 to 60 minutes. Most of this time is spent getting ready for the scan. The actual test takes a few minutes.
What happens after the test?
- You will probably be able to go home right away.
- You can go back to your usual activities right away.
- If dye was used, drink lots of liquids for 24 hours after the test, unless your doctor says not to.

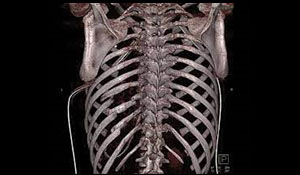
CT SCAN EXTREMITIES/SKELETON
The extremity CT scan is the diagnostic method of the examination of the limbs’ abnormalities of skeletal structure, and the degenerative, bone lesions of the joints. The extremity CT scan is also suitable for the detection of lesions caused by injuries and bone tumors.
Extremity CT is used to examine the femur, knee, shin, ankle, foot, shoulder, upper arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand.



