Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound involves the use of sound waves whose echoes are used to produce images. It is not associated with any radiation exposure and so it is completely safe in pregnancy.
With ultrasound we can be able to image the following systems:
- Cranial ultrasound-for children less than one year
- Thyroid ultrasound
- Abdominal Ultrasound
- Hepatobiliary Ultrasound
- Pelvic Ultrasound
- Obstetric Ultrasound
- Prostate Ultrasound
- Doppler Ultrasound
- Ultrasound guided interventional procedures
Ultrasound technology is excellent at visualizing soft tissues, such as organs and muscles.
Detailed Ultrasound info
ABDOMINAL ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Prior study:
Liver:
Liver is normal in size with a smooth contour. The parenchyma is homogeneously echogenic. No solid or cystic mass is seen.
Intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts are not dilated with common bile duct measuring ….. mm.
Portal vein is of normal caliber and shows normal respiratory variation.
Gallbladder:
The gall bladder is well visualized and appears normal. Wall thickness is……..mm which is within normal limits. There is no peri-cholecystic fluid or cholelithiasis. No tenderness is elicited over the gallbladder.
Pancreas:
The head, body, and tail appear normal in size and echogenicity. No obvious mass is seen.
Pancreatic duct is normal in caliber
Spleen:
Spleen is normal in size and echogenicity.
It measures ….. (L) x …….( AP) x ……(W) cm
Kidneys:
Both kidneys are normal in site, size and orientation.
Right kidney measures … cm (L) x …..cm (W)
Left kidney measures … cm (L) x ……cm (W)
There is no pelvicalyceal dilatation or nephrolithiasis.
No cystic or solid mass lesion is seen.
Aorta & Inferior vena cava:
The visualized portions appear normal
There is no free fluid in the pouch of Douglas, hepatorenal and splenorenal recesses.
IMPRESSION:
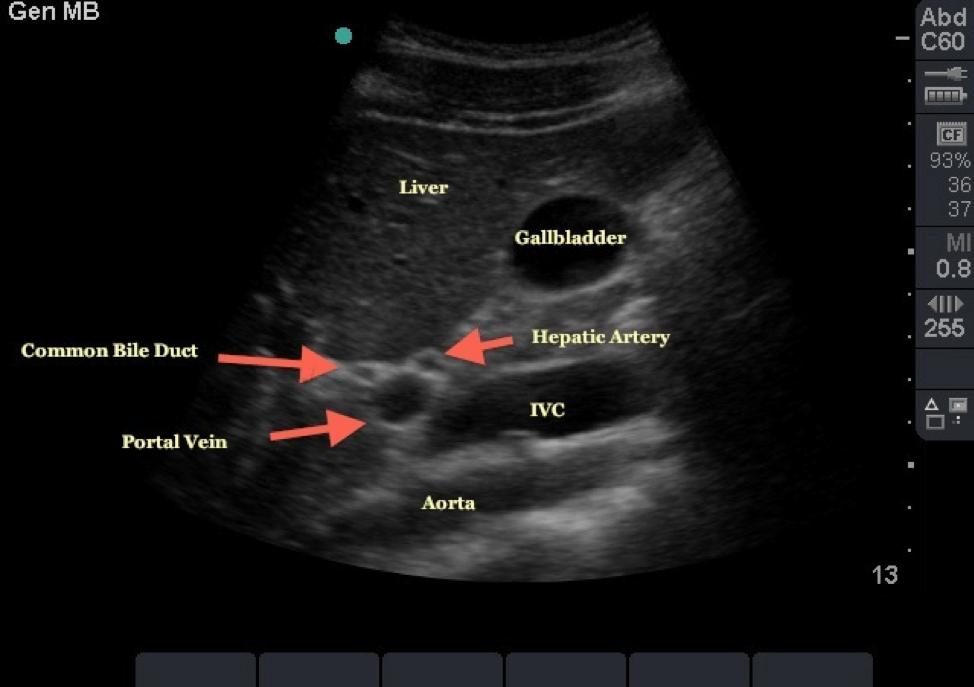
HEPATOBILIARY ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Prior Study:
Liver:
Liver is normal in size with a smooth contour. The parenchyma is homogeneously echogenic. No solid or cystic mass is seen.
Intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts are not dilated with common bile duct measuring ….. mm.
Portal vein is of normal caliber and shows normal respiratory variation.
Gallbladder:
The gall bladder is well visualized and appears normal. Wall thickness is……..mm which is within normal limits. There is no peri-cholecystic fluid or cholelithiasis. No tenderness is elicited over the gallbladder.
Pancreas:
The head, body, and tail appear normal in size and echogenicity. No obvious mass is seen.
Pancreatic duct is normal in caliber
Spleen:
Spleen is normal in size and echogenicity.
It measures ….. (L) x …….( AP) x ……(W) cm
There is no free fluid in the hepatorenal recess.
IMPRESSION:
RENAL ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Prior Study:
Technique:
The kidneys and bladder were evaluated at real-time sonographically with static gray scale images obtained for image documentation.
Findings:
The right kidney is normal in location, contour and length, measuring …. cm.
The renal parenchyma is of normal echogenicity
There is no stone or renal mass.
There is no focal parenchymal thinning or hydronephrosis.
The left kidney is normal in location, contour and length measuring ….. cm.
The renal parenchyma is of normal echogenicity
There is no stone or renal mass.
There is no focal parenchymal thinning or hydronephrosis.
There is no distal ureteral dilatation at the level of the moderately distended urinary bladder.
Bladder wall thickness is within normal limits and no mural lesion is seen.
No bladder calculus is evident.
The visualized portions of the IVC and abdominal aorta are normal.
IMPRESSION: Normal renal ultrasound.
PAEDIATRIC RENAL ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Prior Study:
Technique:
The kidneys and bladder were evaluated at real-time sonographically with static gray scale images obtained for image documentation.
Findings:
Mean renal length for age is …… cm (+/- ……. cm for two standard deviations).
The right kidney is normal in location, contour and length, measuring …. cm.
The renal parenchyma is of normal echogenicity
There is no stone or renal mass.
There is no focal parenchymal thinning or hydronephrosis.
The left kidney is normal in location, contour and length measuring ….. cm.
The renal parenchyma is of normal echogenicity
There is no stone or renal mass.
There is no focal parenchymal thinning or hydronephrosis.
There is no distal ureteral dilatation at the level of the moderately distended urinary bladder.
Bladder wall thickness is within normal limits and no mural lesion is seen.
No bladder calculus is evident.
The visualized portions of the IVC and abdominal aorta are normal
IMPRESSION: Normal renal ultrasound with appropriate renal growth for age
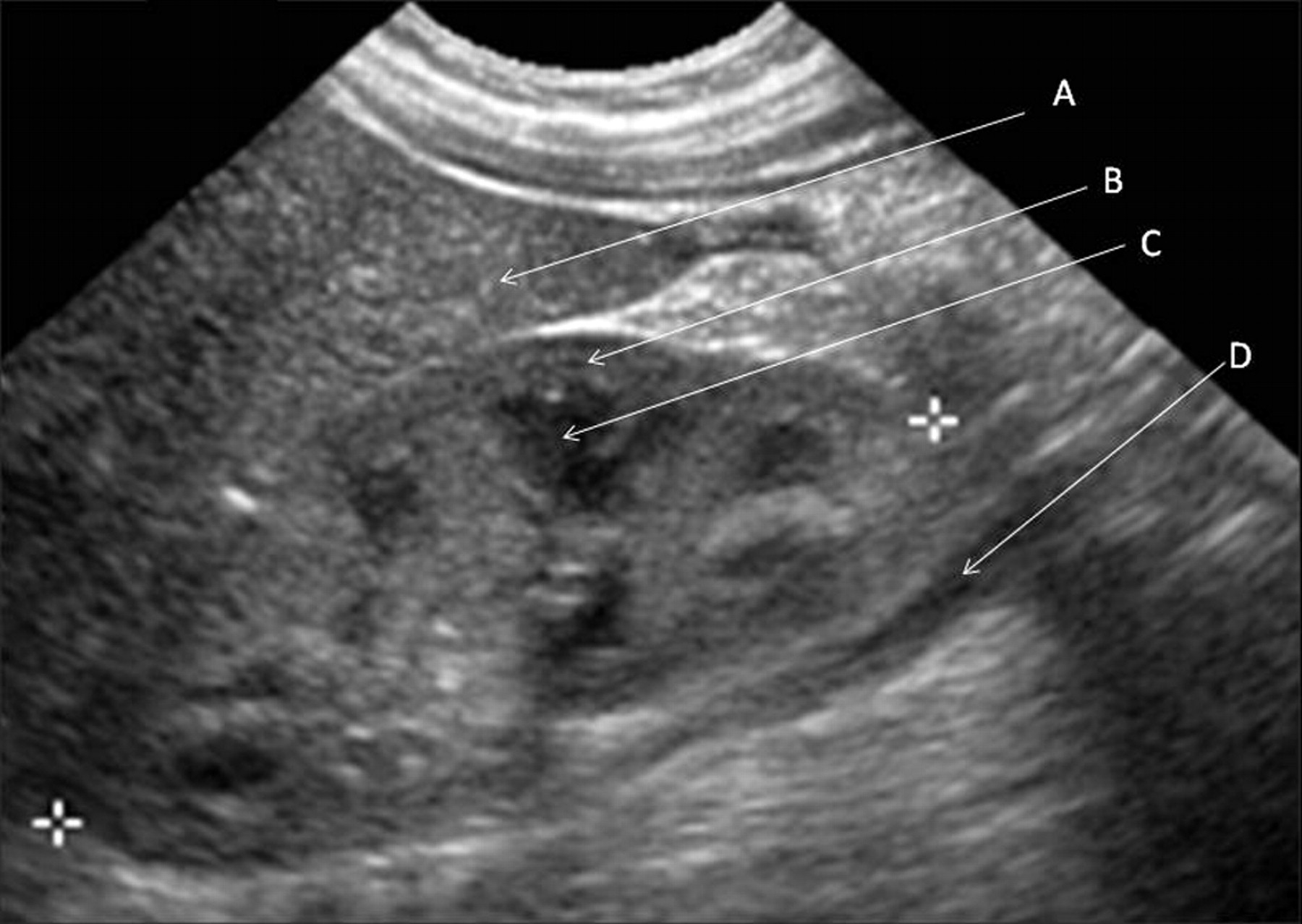
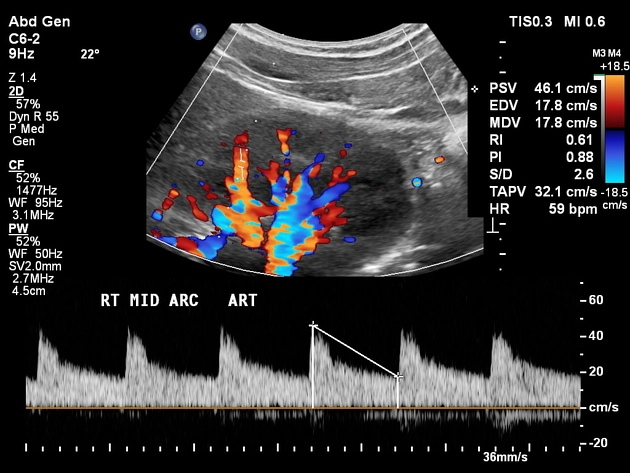
RENAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
History:
Comparison:
Technique:
Complete renal real-time scan with image documentation. Renal vessels and abdominal aorta are evaluated color-flow and spectral waveform analysis Doppler.
Findings:
The right kidney is normal in location, contour and length, measuring …. cm.
The renal parenchyma is of normal echogenicity
There is no stone or renal mass.
There is no focal parenchymal thinning or hydronephrosis.
The left kidney is normal in location, contour and length measuring ….. cm.
The renal parenchyma is of normal echogenicity
There is no stone or renal mass.
There is no focal parenchymal thinning or hydronephrosis.
Doppler evaluation:
Right kidney:
Peak systolic velocities in the main renal artery measure as follows:
Ostium: …………cm/sec.
Proximal:…………cm/sec.
Mid:……………….cm/sec.
Distal:………….…cm/sec.
Intrarenal resistive indices range from ….. to …….
The right main renal vein is patent and demonstrates a normal waveform.
Left kidney:
Peak systolic velocities in the main renal artery measure as follows:
Ostium:……………..cm/sec.
Proximal:…….…….cm/sec.
Mid:…………………cm/sec.
Distal:……………….cm/sec.
Intrarenal resistive indices range from ….. to ……
The left main renal vein is patent and demonstrates a normal waveform.
The visualized portions of the IVC and abdominal aorta are normal.
There is no distal ureteral dilatation at the level of the moderately distended urinary bladder.
Bladder wall thickness is within normal limits and no mural lesion is seen.
No bladder calculus is evident.
IMPRESSION: Normal renal ultrasound with Doppler
PELVIC ULTRASOUND
Clinical History: [LMP: date]
Study:[transabdominal / transvaginal ultrasound of pelvis]
Uterus:
The uterus is [anteverted/retroverted] and measures ……cm (L) x……cm(AP) x …….cm(W). No mass lesion is seen.
The endometrial thickness is ……. mm which is within normal limits.
The cervix appears normal.
Ovaries:
Right ovary measures …..mm (L) x ……mm (AP) x …….mm(W)
Left ovary measures …..mm (L) x ……mm (AP) x …….mm(W)
No cystic or solid adnexal mass is seen.
No free fluid is seen in the pouch of Douglas.
OBSTETRIC ULTRASOUND FIRST TRIMESTER
Clinical History:
LMP:
Study: [transabdominal/transvaginal ultrasound of pelvis]
Uterus:
The uterus is [anteverted/ retroverted] and gravid with a single gestation.
The cervix appears normal and the internal os is closed.
Gestation:
The yolk sac and foetal pole are visualized and appear normal.
Crown-rump length (CRL) is ……. mm which corresponds to a mean gestational age of ……weeks…….. days. Gestational age by LMP is ….weeks…..days.
Nuchal translucency is …… mm which is within normal limits.
Foetal heart rate is …… bpm and regular.
The embryo appears grossly normal.
Normal trophoblastic reaction is seen.
Ovaries:
Right ovary measures …..mm (L) x ……mm (AP) x …….mm(W)
Left ovary measures …..mm (L) x ……mm (AP) x …….mm(W)
Adnexa are clear.
No free fluid is seen in the pouch of Douglas.
IMPRESSION:
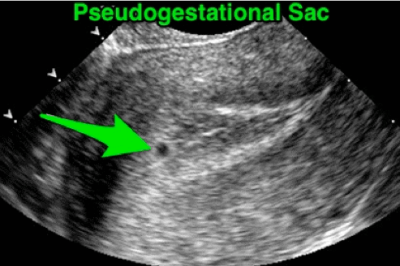
OBSTETRIC ULTRASOUND ANOMALY SCAN
Clinical History:
L.M.P.:
Comparison:
Findings:
A single intra-uterine gestation is seen.
Foetal cardiac activity is present and regular with a heart rate of …… bpm.
Biometric profile:
BPD = mm which corresponds to weeks days
HC = mm which corresponds to weeks days
AC = mm which corresponds to weeks days
FL = mm which corresponds to weeks days
Brain shows normal ventricles with normal lateral ventricle width. The cerebella diameter is normal for gestation. Cisterna magna has a normal width.
Foetal anatomy:
The cranium, cerebral ventricles, cavum septum pellucidum, the midline falx, the choroid plexus are all normal. Posterior fossa structures are normal.
The orbits, lips, hard palate and nasal bone are all normal.
Spine has normal outline from the cranio-vertebral junction to the sacrum with no obvious defect noted.
Heart is normal in situs and has four normal chambers and ventricular outflow tracts are normal.
Thorax has normal shape and echopattern with an intact diaphragm.
No abdominal wall defects are visualized. The stomach, bowel, bladder and kidneys are all normal.
Umbilical cord has three vessels and shows normal attachment to the abdomen. Both upper and lower extremities have normal three long bones. Hands and feet are seen.
Placenta is ……………….and not low lying.
Amniotic fluid is adequate for gestational age.
Maternal anatomy:
Cervix is grossly normal and internal os is closed
No obvious adnexal mass lesion is seen.
The bladder is normal in outline.
Estimated gestational age by Ultrasound = weeks days
Estimated gestational age by LMP= weeks days
IMPRESSION: Normal single intrauterine gestation at ….… weeks ……… days.
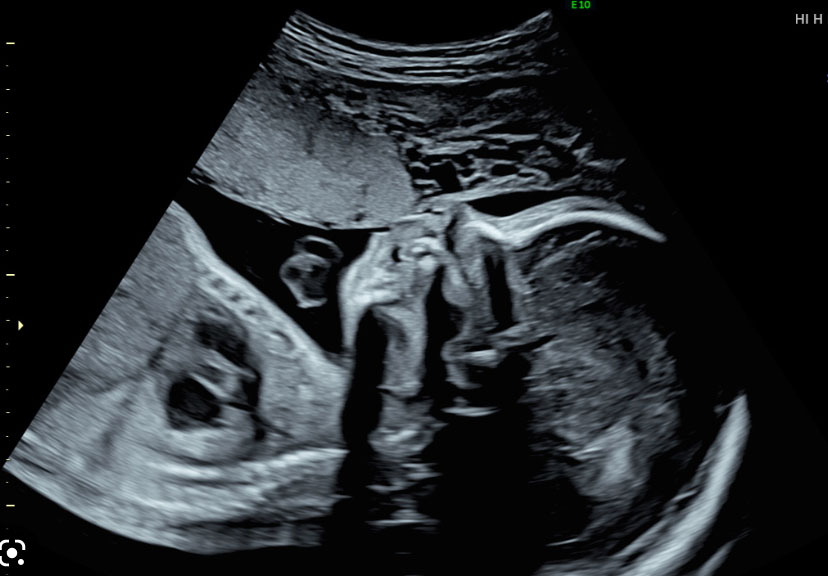
OBSTETRIC ULTRASOUND THIRD TRIMESTER
Clinical history:
LMP:
Comparison:
Findings:
A [single/multiple] intra-uterine gestation is seen in [cephalic/breech] presentation.
Foetal cardiac activity is present and regular with a heart rate of …… bpm.
Biometric profile:
BPD = mm which corresponds to weeks days
HC = mm which corresponds to weeks days
AC = mm which corresponds to weeks days
FL = mm which corresponds to weeks days
Estimated foetal weight is ……. Grams
Normal foetal movements are noted and no gross morphological abnormality is seen.
Amniotic fluid is adequate for gestational age, with an AFI of ……. (Normal=……..)
Placenta is ……………….and not low lying.
Estimated gestational age by Ultrasound = weeks days
Estimated gestational age by LMP= weeks days
IMPRESSION: Normal single intrauterine gestation at ….… weeks ……… days
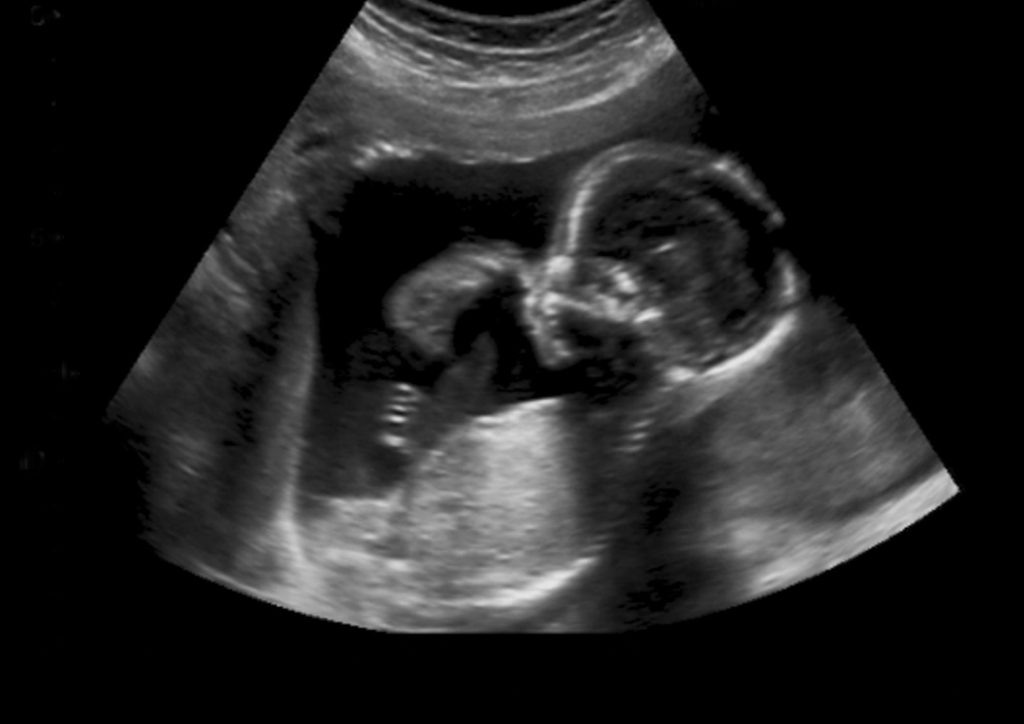
BIOPHYSICAL PROFILE/DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
Clinical history:
LMP:
Comparison:
Findings:
A [single/multiple] intra-uterine gestation is seen in [cephalic/breech] presentation.
Foetal cardiac activity is present and regular with a heart rate of …… bpm.
Biometric profile:
BPD = mm which corresponds to weeks days
HC = mm which corresponds to weeks days
AC = mm which corresponds to weeks days
FL = mm which corresponds to weeks days
Estimated foetal weight is ……. grams
Biophysical profile:
Foetal movement =
Foetal tone =
Foetal breathing =
Amniotic fluid index =
Foetal heart reactivity=
Doppler flows:
Normal Doppler flows are recorded within the umbilical artery. Resistive index measures 0….
Normal Doppler flows are recorded within the middle cerebral artery. Resistive index measures 0….
Placenta is ……………….and not low lying.
Estimated gestational age by Ultrasound = weeks days
Estimated gestational age by LMP= weeks days
IMPRESSION: Normal single intrauterine gestation at ….… weeks ……… days.
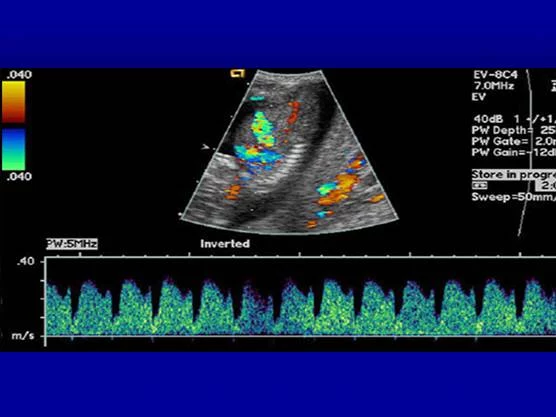
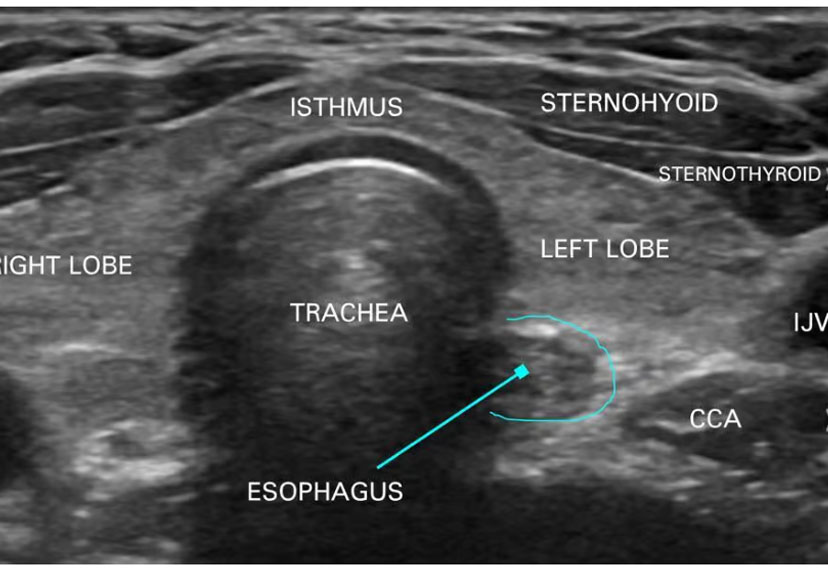
THYROID ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Technique:
Multiple real time longitudinal and transverse images were obtained using a high
resolution ultrasound with a linear transducer.
Findings:
The thyroid gland is normal in site and size.
There is no retrosternal or retrotracheal extension of the gland.
The right lobe measures ……cm (L) x …..cm (AP) x ……cm (W)
The left lobe measures ……cm (L) x …..cm (AP) x ……cm (W)
The isthmus is of normal thickness.
Thyroid parenchyma is homogeneously echogenic.
No focal nodule is seen.
The glandular capsule is intact.
There is no significant cervical lymphadenopathy.
IMPRESSION:
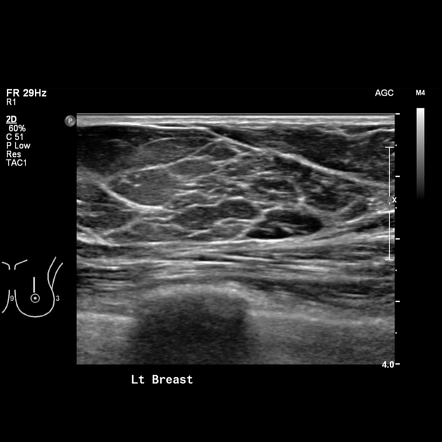
BREAST ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
LMP:
Technique:
Multiple real time longitudinal and transverse images were obtained using a high resolution ultrasound with a linear transducer.
Findings:
The breast parenchyma is predominantly [fatty/fibroglandular/fibrocystic].
No focal solid or cystic lesion is seen.
The intra-mammary ducts are not dilated. No obvious calcification is present.
The axillary tail is normal.
There is no skin thickening or nipple retraction.
No significant axillary lymphadenopathy is seen.
IMPRESSION:
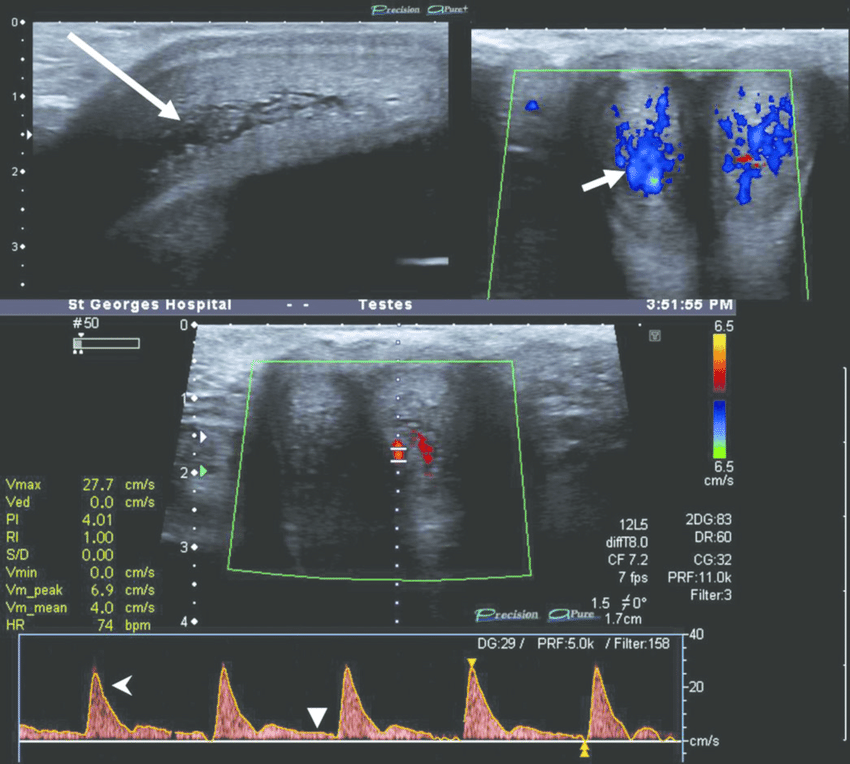
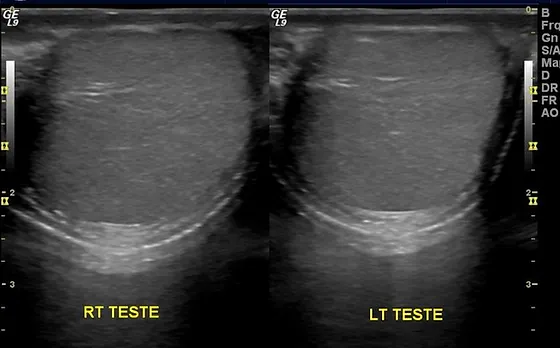
SCROTAL ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Technique:
Multiple real time longitudinal and transverse images were obtained using a high resolution ultrasound with a linear transducer. Doppler ultrasound was also performed.
Findings:
Both testes and epididymis are normal in size and echogenicity.
No focal solid or cystic lesion is seen.
Right testicle measures …….cm x ……cm x …..cm
Left testicle measures …….cm x ……cm x …..cm
Blood flow is normal and symmetrical bilaterally.
No hydrocele or varicocele is present.
IMPRESSION:
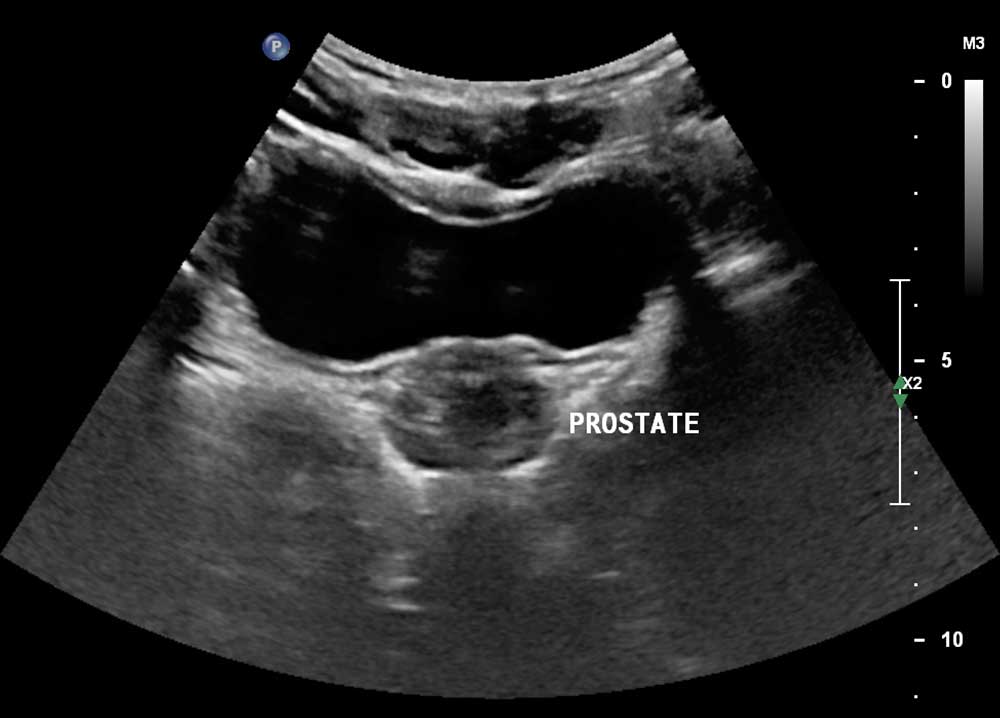
PROSTATE ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Technique:
Multiple real time longitudinal and transverse images were obtained using a high resolution intra-cavitary probe. Doppler ultrasound was also used.
Findings:
Peripheral zone:
The parenchyma is of normal echogenicity. No focal nodule is seen. The prostatic capsule is intact.
Central gland:
The central gland is heterogeneously echogenic. No focal nodule or calcification is seen. No indentation of the bladder base is noted.
Seminal vesicles:
The seminal vesicles are symmetrical and of normal echogenicity. No focal lesion or calcification is seen within them.
Doppler ultrasound does not reveal any abnormal vascularity.
The prostate gland volume is ……mls (grams)
The prostatic urethra appears normal.
Post-micturition volume is …….. mls.
No significant peri-prostatic lymph nodes are noted.
IMPRESSION:
TRANSCRANIAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Technique:
Multiple real time sagittal and coronal images were obtained using a high resolution linear transducer. Doppler ultrasound was used in assessment of cerebral circulation.
Findings:
No gross morphological abnormality is seen.
Cortical folding is appropriate for gestational age.
The grey-white matter differentiation is preserved. Cerebral grey matter is of normal echogenicity.
Normal echogenicity and homogeneity of the periventricular and subcortical white matter is demonstrated.
The thalami and basal ganglia are normal.
The size, width, lining and echogenicity of the ventricular system appears normal.
The widths of the subarachnoid spaces are appropriate for age.
There is no midline shift.
No peri- or intra-ventricular hemorrhage is seen.
IMPRESSION:
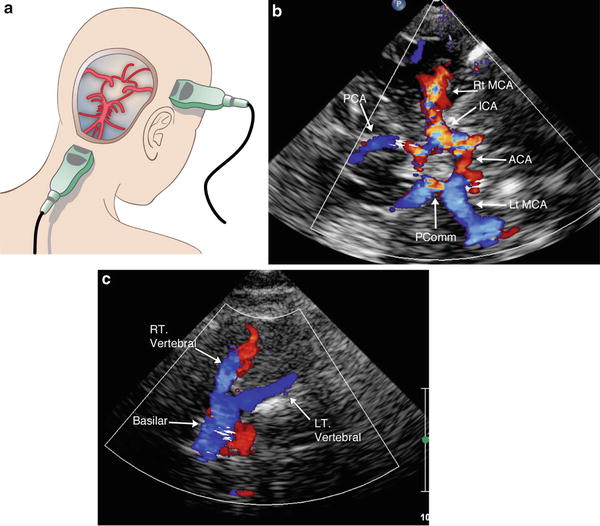
CAROTID DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Technique:
Multiple real time sagittal and coronal images were obtained using a high resolution linear transducer. Doppler ultrasound was used in assessment of cerebral circulation.
Findings:
No gross morphological abnormality is seen.
Cortical folding is appropriate for gestational age.
The grey-white matter differentiation is preserved. Cerebral grey matter is of normal echogenicity.
Normal echogenicity and homogeneity of the periventricular and subcortical white matter is demonstrated.
The thalami and basal ganglia are normal.
The size, width, lining and echogenicity of the ventricular system appears normal.
The widths of the subarachnoid spaces are appropriate for age.
There is no midline shift.
No peri- or intra-ventricular hemorrhage is seen.
IMPRESSION:

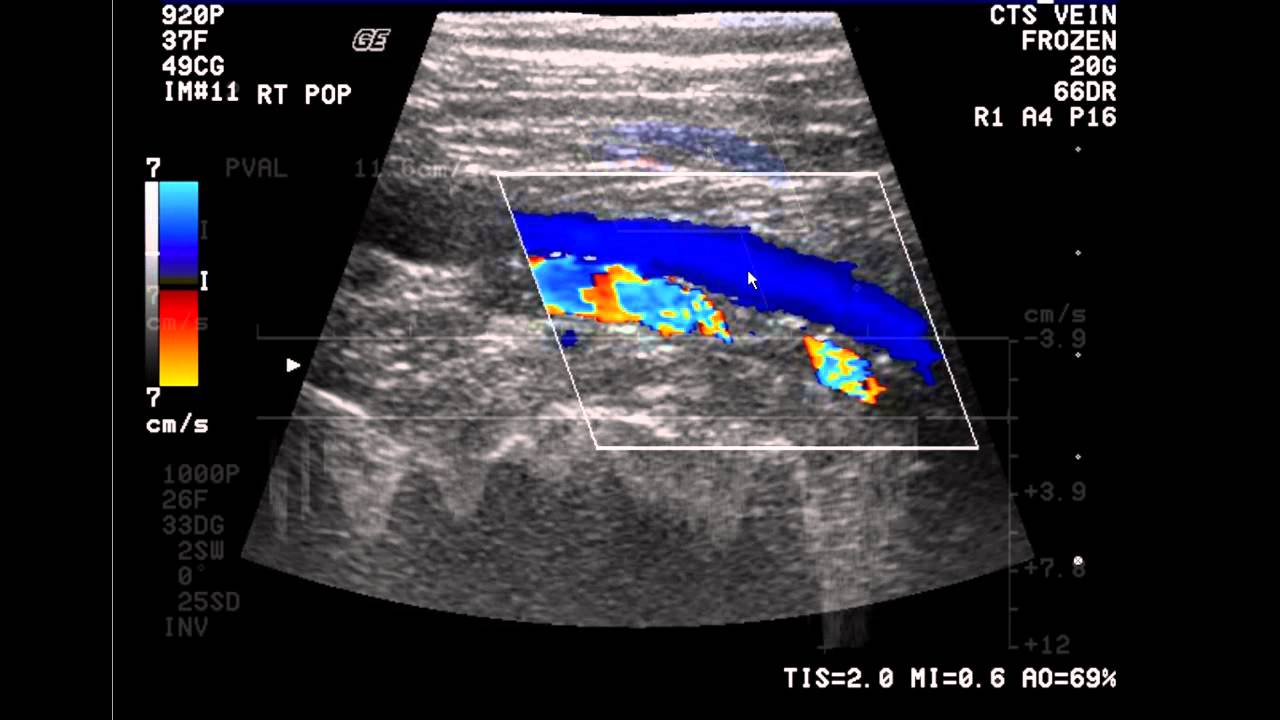
LOWER LIMB VENOUS DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Technique: Triplex Doppler ultrasonography of the lower limb veins using a high frequency linear transducer.
Findings:
Right:
Normal Doppler flows with respiratory phasicity are demonstrated in the distal external iliac, common femoral, femoral and popliteal veins.
The vessels are all compressible and no thrombus is seen.
Both the sapheno-femoral and popliteo-femoral venous junctions appear normal.
No significant venous insufficiency is noted.
Left:
Normal Doppler flows with respiratory phasicity are demonstrated in the distal external iliac, common femoral, femoral and popliteal veins.
The vessels are all compressible and no thrombus is seen.
Both the sapheno-femoral and popliteo-femoral venous junctions appear normal.
No significant venous insufficiency is noted.
IMPRESSION: There is no evidence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT).
Essentially normal lower limb venous Doppler ultrasound.
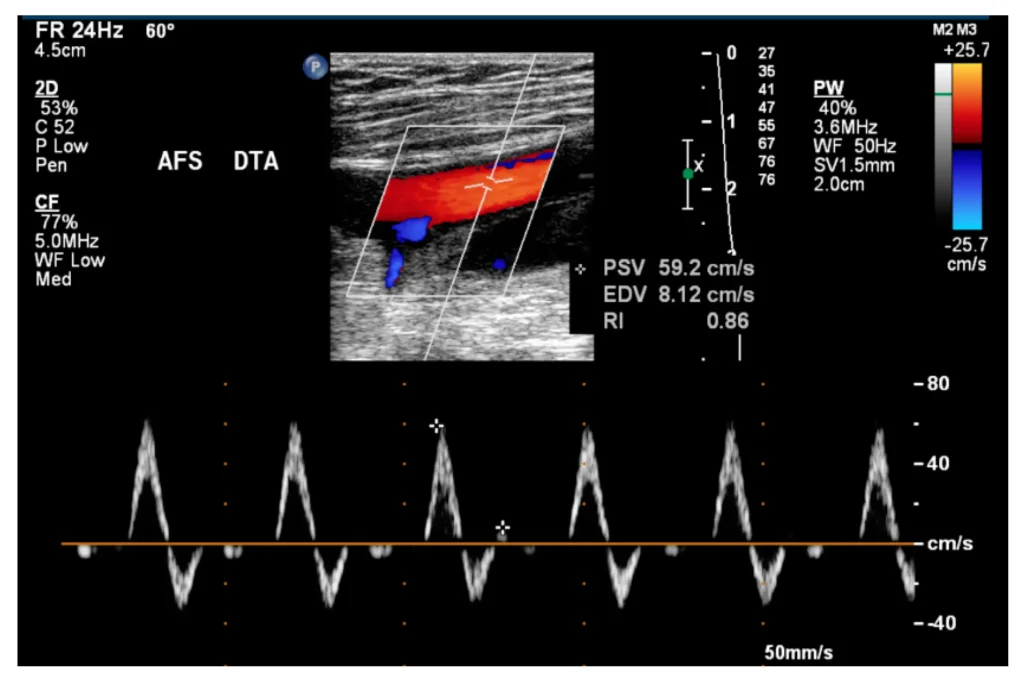
LOWER LIMB ARTERIAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Technique: Triplex Doppler ultrasonography of the lower limb arteries using a high frequency linear transducer
Findings:
Right:
Normal pulsatile triphasic waveform pattern is demonstrated in the distal external iliac, common femoral, femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis arteries.
No significant atheromatous plaque formation is observed.
Intimal lining is smooth and regular.
No aneurism is seen.
Spectral analysis is entirely normal.
There is no focal area of stenosis or thrombosis noted.
Left:
Normal pulsatile triphasic waveform pattern is demonstrated in the distal external iliac, common femoral, femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis arteries.
No significant atheromatous plaque formation is observed.
No aneurism is seen.
Intimal lining is smooth and regular.
Spectral analysis is entirely normal.
There is no focal area of stenosis or thrombosis noted.
A summary of the flow velocities and ratios is attached.
Impression: Essentially normal lower limb arterial Doppler ultrasound. No significant atheromatous plaque formation, stenosis, aneurysm or thrombosis is observed.
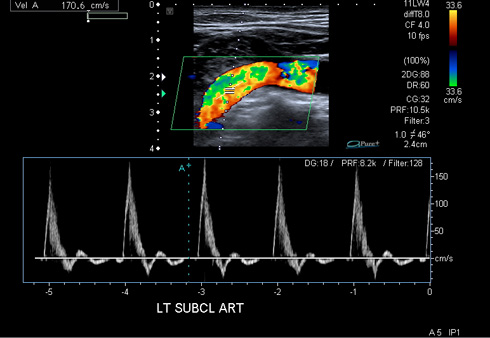
UPPER LIMB ARTERIAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Technique: Triplex Doppler ultrasonography of the upper limb arteries using a high frequency linear transducer.
Findings:
Right:
Normal pulsatile triphasic waveform pattern is demonstrated in the subclavian, axillary, brachial, ulnar and radial arteries.
No significant atheromatous plaque formation is observed.
Intimal lining is smooth and regular.
No aneurysm is seen.
Spectral analysis is normal.
There is no focal area of stenosis or thrombosis noted.
Left:
Normal pulsatile triphasic waveform pattern is demonstrated in the subclavian, axillary, brachial, ulnar and radial arteries.
No significant atheromatous plaque formation is observed.
No aneurysm is seen.
Intimal lining is smooth and regular.
Spectral analysis is entirely normal.
There is no focal area of stenosis or thrombosis noted.
A summary of the flow velocities and ratios is attached.
Impression: Essentially normal upper limb arterial Doppler ultrasound. No significant atheromatous plaque formation, aneurysm, stenosis or thrombosis is observed.
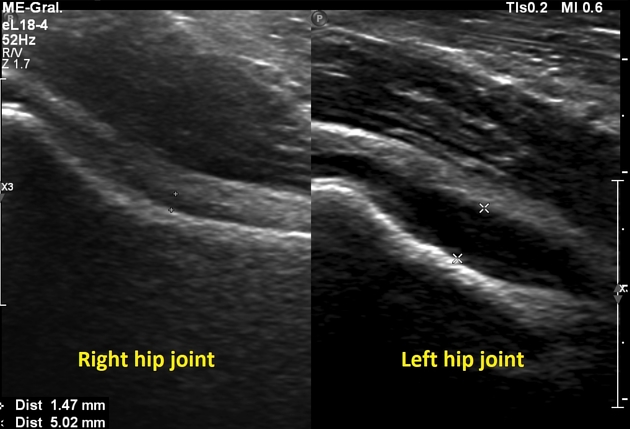
HIP ULTRASOUND
Clinical History:
Technique: Dynamic bilateral hip ultrasound was performed using gray-scale imaging.
Comparison:
Findings:
There is no hip dislocation or subluxation.
No increased motion with stress maneuvers is present.
Both femoral heads are within the acetabula.
The right alpha angle is ………..degrees.
The left alpha angle is ………… degrees.
IMPRESSION: Normal bilateral hip ultrasound.
SCROTAL/PENILE DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
Clinical History: E.D.
Technique:
Multiple real time longitudinal and transverse images were obtained using a high resolution ultrasound with a linear transducer. Doppler ultrasound was also performed.
Findings:
Both testes and epididymis are normal in size and echogenicity.
No focal solid or cystic lesion is seen.
Right testicle measures …….cm x ……cm x …..cm
Left testicle measures …….cm x ……cm x …..cm
Blood flow is normal and symmetrical bilaterally.
No hydrocele or varicocele is present.
Both corpora carvernosa are of homogenous echogenicity. No focal lesion is seen within the corpora. The corpus spongiosum is homogenously hypoechoic and the penile urethra appears normal.
The Doppler Flows are as follows:
Right:
The maximal arterial systolic velocity in the flaccid state is while the end diastolic velocity is
Following arousal, the maximal arterial systolic velocity in the flaccid state is while the end diastolic velocity is
Left:
The maximal arterial systolic velocity in the flaccid state is while the end diastolic velocity is
Following arousal, the maximal arterial systolic velocity in the flaccid state is while the end diastolic velocity is
IMPRESSION:
Findings described are suggestive of an arterial inflow/venous outflow dysfunction.